Sisujuht
Objects
Objects are persistent analytic phenomena that define some analytic characteristics set to report on. Depending on the customer's business specifics and needs, the set can be, for example
- structure of company's departments - sales department, finance department, administration, logistics department, personnel department etc. i.e. if it is necessary to differentiate incomes/expenses at departments level.
- structure of subdivisions - if you need a more detailed overview by departments
- structure of sales regions - Europe, Asia, America, etc.
- product group identifier - when it is necessary to analyze incomes and costs by different product groups
- persons - calculation of costs related to employees
- cars - calculation of costs related to cars
A suitable object level structure is necessary for reporting. Object moves between different modules (sales, book, etc.) in the reports. For example, looking at the income statement, it is the smallest entity. The object can be placed on: user, customer, item or item class.
object levels must be created before objects:
Settings → Finance → Object levels.
Object levels are necessary so that several different levels objects can be attached to one income or expense transaction. Same level objects cannot be placed more than one at a time.
For example, Store 1 cannot be located in Tallinn and Tartu at the same time.
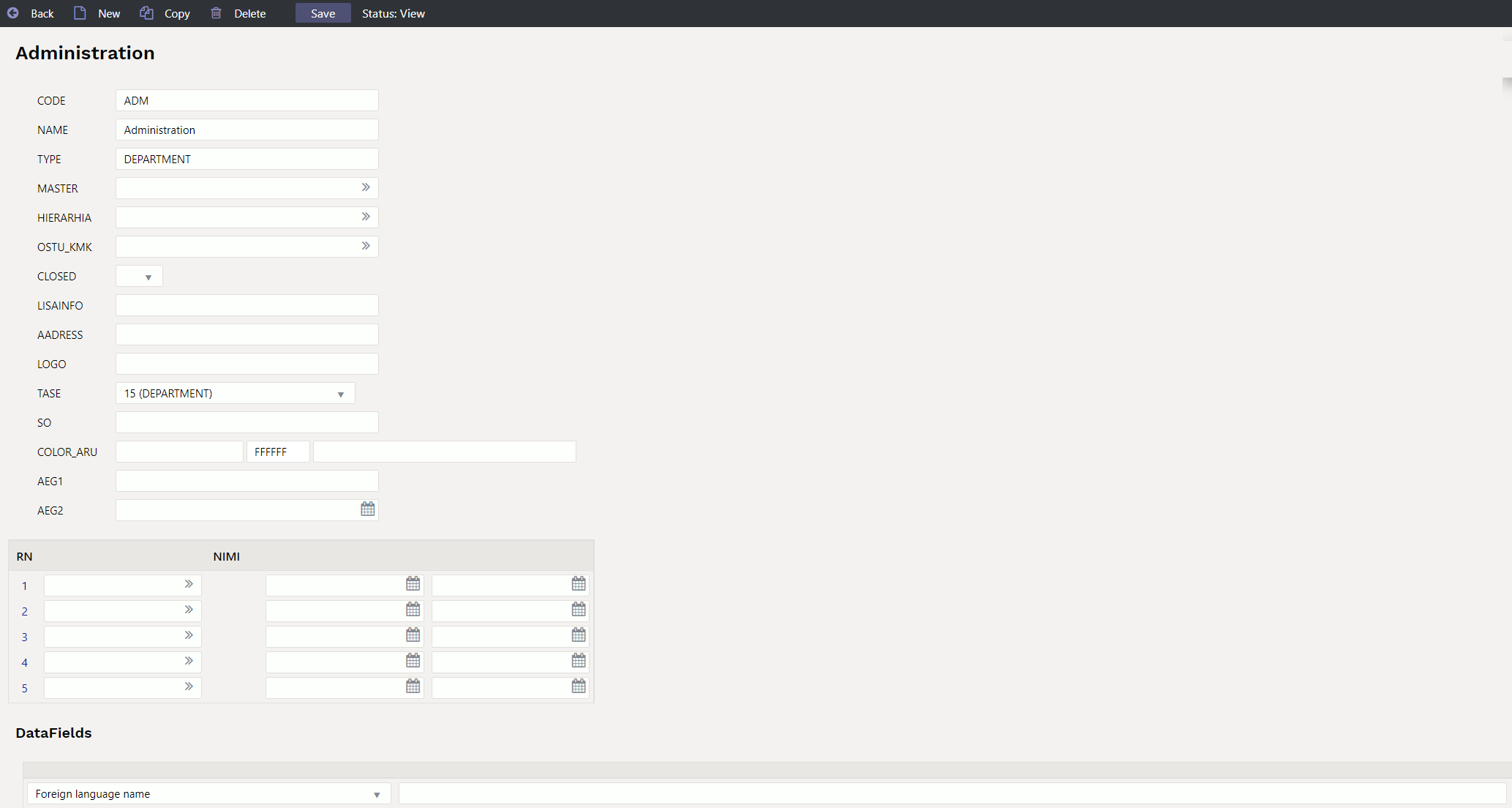
1. Object card
1.1. Header fields
- Code- object short code
- Name- objects name
- Type- displays reports by object types (levels). If the system setting
Object type will be Object Levels nameis enabled, then by default the object level name always becomes the name of the type after selecting the level and saving the object. - Master - helps review the reporting. You don't even have to enter the document anywhere.
- Hierarchy - an object that is placed associated with this object and additionally its associated object is also placed, for example, a department on the person's object card, and if an object is also added to the department's object in the hierarchy field, then this object is also placed.
- Hierarchies- objects that are always placed with this object. Objects are entered separated by commas.
- Purchase VAT code- you can select the purchase VAT code related to this object
- Closed- option to close the object. Object option can be used in reports but not on documents.
- Level- in finance settings you can create levels for objects, for example: department, employees.
- Order- by default, the objects are sorted by code, but if is wanted the objects to be in a different order in the placer, you can enter the objects order numerically in this field.
- Colour in reports- possible to assign a colour to an object if is wanted that object is displayed in a different colour in reports.
- Valid from ja Valid until - can be applied if is wanted to limit the use of the object in time. The verification is performed to the time of the document.
1.2. Related objects
Related objects can be assigned to objects to simplify object placement and avoid false connections.
- Object - selection from the object register;
- Name - shows related object name;
- Level - shows related object level;
- Start - relation start date (if empty, the entire past is considered as the beginning);
- End - relation end date (if empty, the entire past is considered as the end).
Use
Object relations act as a object selection restriction in the matrix setter. The object matrix setter considers related objects as follows:
- If an object with related objects is selected in the matrix, then in other levels where there are objects related to this object, only related objects are shown;
- If several selected objects have relations within the same level, then common part is shown in that level;
- If the object selected to the matrix has an effect through related objects to a level where the object is already selected, but the restriction does not include the previously selected object, then it is deleted from the matrix;
- If an object does not have any related object, then it also does not restrict any level in the matrix;
- An additional limitation is the Start and End assigned to the related object;
- To apply the time filter, it is compared whether the document time remains in the period specified in the relation.
- Time filter Start and/or End may be blank. Then they are used as the beginning of time or infinity.
The objects relation is also checked when confirming documents. In case of errors, a corresponding message is given and confirmation is not successful.
2. Settings
Settings → System settings → Common settings
- Is object paster a matrix one: Yes/No- by default the setting is No and the placer is a list. If an object has more than one level, the setting must be set to YES.
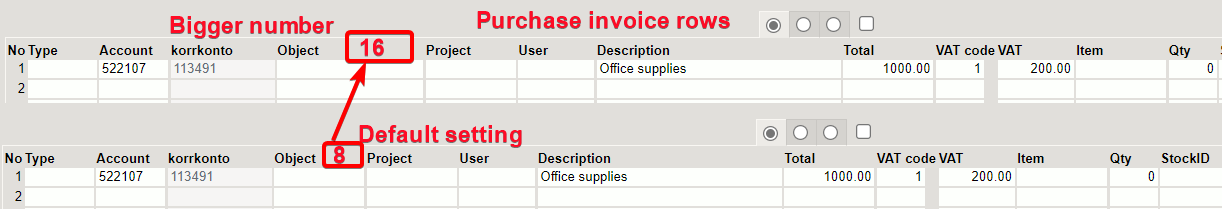
- Object code field size: by default is 8. A larger number expands the width of the field in the document rows.
Settings → System settings → Finance settings
- Object type will be Object Levels name: Yes/No- by default the setting is No. If you select Yes, then by default the object level name will always be the type name after selecting the level and saving the object.
Settings → System settings → Administrator settings
- Object hierarchies are editable: Yes/No - by default the setting is No, then object relations can be created as a hierarchy on the object card. If you select Yes, it is possible to define for each object personally which specific levels objects go here.
3. User rights
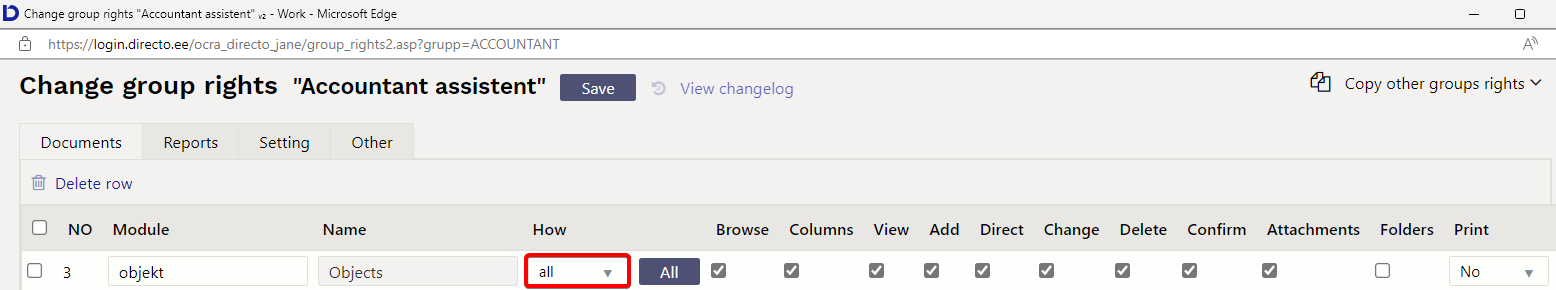
The right to use objects can be given
Settings → Common settings → User groups → Documents
Add module.
Select from How column All and give rigths to just only view or add, change and delete. Own and extended options are not in use.